Bài này là nội dung dịch từ bài báo "Comparison of Ontology Editors" của tác giả Emhimed Salem Alatrish, đăng trên tạp chí eRAF Journal on Computing.
Tóm tắt
Trong bài báo nay thực hiện việc review và đánh giá, so sánh các công cụ phần mềm có liên quan đến web ngữ nghĩa. Theo đó, bài báo này thực hiện việc đánh giá và so sánh 5 công cụ phần mềm biên tập ontology. 5 phần mềm này bao gồm: Apollo, OntoStudio, Protégé, Swoop và TopBraid Composer Free Edition. Cấu trúc và các đặc điểm cơ bản của các công cụ biên tập ontology này đã được mô tả cũng như các thức sử dụng chúng. Tiêu chí chính để đánh giá và so sánh các công cụ phần mềm này là tính tiện lợi với người sử dụng và khả năng áp dụng trong các loại ứng dụng khác nhau.
I. Giới thiệu
Có rất nhiều công cụ phần mềm liên quan đến web ngữ nghĩa. Các công cụ phần mềm web ngữ nghĩa đặc biệt là các công cụ phần mềm tạo lập và thao tác với ontology. Có thể tìm thấy rất nhiều phần mềm biên tập ontology trên Internet. Một vài trong số các công cụ đó (ví dụ như: Apollo, OntoStudio, Protégé, Swoop và TopBraid Composer Free Edition) được sử dụng tương đối rộng rãi (Ví dụ, trong [1], công cụ biên tập web ngữ nghĩa Protégé được xếp vào danh mục “killer application” trong đó "killer applications" được định nghĩa như là các công nghệ chuyển đổi mức cao mà nó tạo ra các thị trường mới và các mẫu hành vi được sử dụng rộng rãi). Đó chính là nguyên nhân sự cần thiết phải có các nghiên cứu để so sánh giữa các công cụ phần mềm biên tập ontology này. Việc so sánh có thể được thực hiện bằng cách sử dụng các tiêu chí so sánh khác nhau: tính phổ biến (generality), Tính diễn cảm (expressiveness), tính phức tạp (complexity), tài liệu hỗ trợ (documentation), tính mở rộng (scalability), ...Trong nghiên cứu của chúng tôi, tiêu chí quan trọng nhất là tính dễ sử dụng và tính phổ biến (spreading) của các công cụ biên tập Ontology. Các công cụ phần mềm biên tập ontology hay được sử dụng nhất là : Apollo (xem [11]), Protégé (xem [14], [16], [6] và [17]), OntoStudio (xem [12] và [13]), TopBraid Composer Free Edition (xem [20], [22] và [21]) và Swoop (xem [18], [19] và [6]) và đó cũng là lý do chính để chúng tôi quyết định chỉ thực hiện việc so sánh giữa các công cụ này.
II. Các nghiên cứu liên quan
Đối với những người nghiên cứu và sử dụng web ngữ nghĩa, việc có một review tổng quan về các công cụ phần mềm web ngữ nghĩa và mối quan hệ giữa chúng là rất quan trọng. Tuy nhiên, việc so sánh giữa các công cụ phần mềm này có thể được thực hiện bằng nhiều cách khác nhau. Có một loạt các bài báo được thực hiện nhằm so sánh giữa các công cụ biên tập ontology (ví dụ: [2], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8] và [9]). Việc so sánh giữa các công biên tập ontology ngoài việc sử dụng các tiêu chí khác nhau còn quan tâm đến các khía cạnh sử dụng khác nhau của các công cụ này. Ví dụ, trong [2] đã thực hiện việc mô tả 20 công cụ web ngữ nghĩa với hơn 10 đặc tính. Trong [3] một công việc kiểm tra đơn giản của việc mô hình hóa và hiển thị đã được sử dụng để so sánh giữa các công cụ biên tập. Một khung nhìn thú vị về các yêu cầu đối với ontology - cuộc cách mạng của các công cụ phần mềm đã được giới thiệu trong [4]. Điểm nhấn trong các yêu cầu chức năng và tác giả đã chia thành 8 yêu cầu quan trọng nhất. Tuy nhiên, ngoài 8 yêu cầu chức năng đó, các yêu cầu phi chức năng cũng đặc biệt được quan tâm.
Chúng tôi đã sử dụng và thử nghiệm với 5 công cụ biên tập ontology (Apollo,OntoStudio, Protégé, Swoop và TopBraid Composer Free Edition) và chúng tôi quyết định xem xét đến ưu điểm và những điều còn thiếu của các công cụ này. Các công cụ này được sử dụng để xây dựng một ontology mới hoặc là từ đầu hoặc là bằng cách sử dụng lại các ontology đã có sẵn, các công cụ này thường hỗ trợ việc biên tập, duyệt, xây dựng tài liệu, export và import ra / từ các định dạng khác nhau, xem và tạo thư viện. Các công cụ này đã được gắn trong các bộ thư viện tham chiếu, bao gồm hỗ trợ cho một vài ngôn ngữ lập trình, ... (xem [5]).
III. Các công cụ phần mềm biên tập, xây dựng Ontology
Chúng tôi sẽ cố gắng cung cấp một cái nhìn tổng quan về một số công cụ biên tập ontology hiện đang được sử dụng để xây dựng ontology. Chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp các mô tả ngắn gọn về các công cụ và giới thiệu các nhóm đã phát triển các công cụ này. Việc so sánh sẽ được thực hiện bằng cách quan tâm đến các thuộc tính khác nhau của các công cụ biên tập ontology này. Chúng tôi sẽ tính đến các đặc điểm sau đây [10].
- Mô tả chung của các công cụ includes information about developers and availability.
- Kiến trúc phần mềm và sự phát triển công cụ includes information about the tool architecture (standalone, client/server, n-tier application). It also explains how the tool can be extended with other functionalities/modules; furthermore, it describes how ontologies are stored (databases, text files, etc.) and if there any backup management system.
- Đồng vận hàng (interoperability) với các công cụ và ngôn ngữ phát triển ontology khác includes information about the interoperability of the tool. Tool‟s interoperability with other ontology tools can be recognized by functionalities like (merging, annotation, storage, inference, etc.), in ad dition to translations to and from ontology languages.
- Biểu diễn tri thức is related to presenting of knowledge model of the tool. It also includes the possibility of providing any language for building axioms and whether tool gives support to methodology.
- Các dịch vụ suy luận attached to the tool tells if the tool has a builtin inference engine or it can use other attached inference engine. It also shows if the tool performs constraint/consistency checking. It also provides the possibility of classifying concepts automatically in concept taxonomy and capabilities to manage the exceptions in taxonomies.
- Tính khả dụng shows the existence of the graphical editors for the creation of concept taxonomies and relations, the ability to prune these graphs and the possibility to perform zooms of parts of it. It also says if the tool allows some kind of collaborative working and whether it provides libraries of ontologies.
- Apollo
- OntoStudio
- Protégé
- Swoop
- TopBraid Composer Free Edition
All these tools are widespread in the ontology design and development sector and are accepted by relatively large semantic web communities. These tools also provide the minimum necessary functionality supporting the ontology development process.
The ontology editors are tools that allow users to visually manipulate, inspect, browse, code ontologies, support the ontology development and maintenance task. In this section, we will provide a broad overview of some of the available ontology editor tools with a brief description of each tool, presenting the group that has developed it, its main features and functionalities, its URL, etc.
A. Apollo
Apollo [11] is a user-friendly knowledge modeling application. Apollo allows a user to model ontology with basic primitives, such as classes, instances, functions, relations and so on. The internal model is a frame system based on the OKBC protocol. The knowledge base of Apollo consists of a hierarchical organization of ontologies. Ontologies can be inherited from other ontologies and can be used as if they were their own ontologies. Each ontology is the default ontology, which includes all primitive classes. Each class can create a number of instances, and an instance inherits all slots of the class. Each slot consists of a set of facets. Apollo does not support graph view, web, information extraction and multi-user capabilities or collaborative processing but it features strong type consistency checking, storing the ontologies (files only) and import/export format (I/O plug-in architecture -export plug-ins to CLOS and OCML). Apollo is implemented in Java and it is available for a download from http://apollo.open.ac.uk/index.html.
B. OntoStudio
OntoStudio is based on IBM Eclipse framework. It can be downloaded for three months free evaluation period. It is an Ontology Engineering Environment supporting the development and maintenance of ontologies by using graphical means. It is based on client/server architecture, where ontologies are managed in a central server and various clients can access and modify these ontologies. It supports multilingual development, and the knowledge model is related to frame-based languages. It supports collaborative development of ontologies. OntoStudio is built on top of a powerful internal ontology model. The tool allows the user to edit a hierarchy of concepts or classes. OntoStudio is based on an open plug-in structure. The internal representation data model can be exported to DAML+OIL, F -Logic,RDF(S), and OXML. Additionally, ontologies can be exported to relational databases via JDBC. OntoStudio can import external data representation in DAML+OIL, Excel, F-logic, RDF(S), database schemas (Oracle,MS-SQL, DB2,MySQL), and OXML. OntoSudio can also import and export OWL files. OntoStudio provides an API for accessing ontologies in an objectoriente fashion. The default API implementation stores ontologies in main memory, but an additional API exists for persistent storage. The inference ngine that OntoStudio uses is OntoBroker (OntoBroker is the result of several years of research and it is now a commercial product). Using this engine, OntoStudio exploits the strength of F-Logic and it can represent expressive rules. OntoStudio supports collaborative ontologies by using the OntoBroker Enhancement Collaborative server [12], [13].
A. Apollo
Apollo [11] is a user-friendly knowledge modeling application. Apollo allows a user to model ontology with basic primitives, such as classes, instances, functions, relations and so on. The internal model is a frame system based on the OKBC protocol. The knowledge base of Apollo consists of a hierarchical organization of ontologies. Ontologies can be inherited from other ontologies and can be used as if they were their own ontologies. Each ontology is the default ontology, which includes all primitive classes. Each class can create a number of instances, and an instance inherits all slots of the class. Each slot consists of a set of facets. Apollo does not support graph view, web, information extraction and multi-user capabilities or collaborative processing but it features strong type consistency checking, storing the ontologies (files only) and import/export format (I/O plug-in architecture -export plug-ins to CLOS and OCML). Apollo is implemented in Java and it is available for a download from http://apollo.open.ac.uk/index.html.
Figure 1 Apollo screenshot
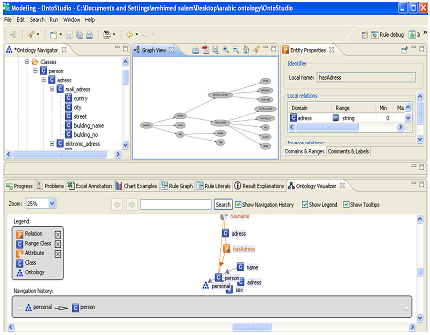
B. OntoStudio
OntoStudio is based on IBM Eclipse framework. It can be downloaded for three months free evaluation period. It is an Ontology Engineering Environment supporting the development and maintenance of ontologies by using graphical means. It is based on client/server architecture, where ontologies are managed in a central server and various clients can access and modify these ontologies. It supports multilingual development, and the knowledge model is related to frame-based languages. It supports collaborative development of ontologies. OntoStudio is built on top of a powerful internal ontology model. The tool allows the user to edit a hierarchy of concepts or classes. OntoStudio is based on an open plug-in structure. The internal representation data model can be exported to DAML+OIL, F -Logic,RDF(S), and OXML. Additionally, ontologies can be exported to relational databases via JDBC. OntoStudio can import external data representation in DAML+OIL, Excel, F-logic, RDF(S), database schemas (Oracle,MS-SQL, DB2,MySQL), and OXML. OntoSudio can also import and export OWL files. OntoStudio provides an API for accessing ontologies in an objectoriente fashion. The default API implementation stores ontologies in main memory, but an additional API exists for persistent storage. The inference ngine that OntoStudio uses is OntoBroker (OntoBroker is the result of several years of research and it is now a commercial product). Using this engine, OntoStudio exploits the strength of F-Logic and it can represent expressive rules. OntoStudio supports collaborative ontologies by using the OntoBroker Enhancement Collaborative server [12], [13].
Figure 2 OntoStudio editor Screenshot

No comments:
Post a Comment